
Bovine Mastitis. Sukolrat Boonyayatra DVM, MS Clinic for Ruminants. What ’ s mastitis ?. Inflammation of one or more quarters of the udder. Mammae = breast -itis = Latin suffix for inflammation. Normal. Inflamed. Swelling pain warm redness. Causes.

lorin + Follow
Download PresentationAn Image/Link below is provided (as is) to download presentation Download Policy: Content on the Website is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use and may not be sold / licensed / shared on other websites without getting consent from its author. Content is provided to you AS IS for your information and personal use only. Download presentation by click this link. While downloading, if for some reason you are not able to download a presentation, the publisher may have deleted the file from their server. During download, if you can't get a presentation, the file might be deleted by the publisher.

Bovine Tuberculosis. Compiled by Sara Moyer, MSU Agriculture and Natural Resources (ANR). Implications. Bovine tuberculosis is a human health issue in many foreign countries where the milk is not pasteurized and there are high rates of human infection
2.83k views • 39 slides

Mastitis: Intramammary Infection IMI. Clinical Mastitis - Animal healthswellingheatrednesspaindisturbed function. Mastitis. Physical appearance - color, flakes, clots, etcpH - normal 6.5 increase to 7 Cellularity - increase in SCCChloride - increase Cl-Catalase - tissue damage - O2 release.
1.22k views • 57 slides

Mastitis. Joe Breuner, M.D. Thanks to . Doug Trotter, who gave this talk 18 months ago. Case Presentation. Healthy 25 year-old woman, G2P2, with a 6 week-old infant Infant is fully breast-fed Patient is fatigued due to caring for 2 young children
1.52k views • 35 slides

bovine. Pertaining to cows or cattle. callow. Young and inexperienced. peccadillo. A minor offense; a misdeed. sagacious. Wise; having keen perception and sound judgment. rationalize. To make an excuse for. fatuous. Foolish; inane. patent. Evident or obvious. laconic.
229 views • 15 slides

Mastitis. Simon Kenyon. Udder anatomy. Udder anatomy. Allometric Growth. Economic Impact. 40% of morbidity on dairy farms Most costly cattle disease in the US Estimated cost to the industry greater than 2 billion dollars/yr Estimated to cost $200-300/cow For herd-based worksheet:
1.5k views • 73 slides

Going Bovine. By: Libba Bray. Genre: Young Readers 14 & UP. Plot.
338 views • 11 slides

Mastitis. Vocabulary. Mastitis -- inflammation of the mammary gland usually caused by microorganisms and bacteria Clinical Mastitis -- visible signs of mastitis Somatic Cell Count– The # of white blood cells in milk. Indication of infection.
912 views • 10 slides
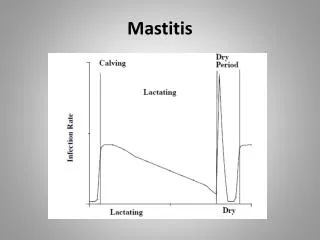
Mastitis. Mastitis Definitions. Mastitis Definitions. Mastitis in Wisconsin. Characteristics of Pathogens. Milking is a Risky Process. The Mammary Infection Process. Clinical Mastitis Symptoms. Mastitis During the Lactation Cycle. Mastitis and Milk Composition.
1.14k views • 49 slides

Mastitis Organisms. Contagious organisms Environmental organisms “Oddball” organisms. Contagious Organisms. Staphylococcus aureus Streptococcus agalactiae Corynebacterium bovis Mycoplasma bovis. Staphylococcus aureus. Invasive pathogen that causes fibrosis and abscesses/microabscesses
475 views • 22 slides

Going Bovine. By: Libba Bray. Genre: Fiction/Young Readers 14 & UP. Summary.
232 views • 11 slides

BOVINE KETOSIS. Peak yield at 4-6 wks but high dry matter intake at 8-10 wks so there will be negative energy balance. Low levels of glucose . Mobilisation of adipose tissue. Increase in NEFA & BHBA. liver. Ketogenesis & gluconeogenesis. Type I:
4.43k views • 23 slides

Bovine Tuberculosis. Dr. Rick Smith Assistant State Veterinarian over Ruminant Programs Bovine TB Program Coordinator MDARD. Overview. Background of Saginaw TB infection Outcomes at infected farms Trace investigation outcomes Circle testing and outcomes
622 views • 20 slides

Bovine Tuberculosis. Overview. Organism History Epidemiology Transmission Disease in Humans Disease in Animals Prevention and Control Actions to Take. The Organism. The Organism. Mycobacterium bovis Gram positive bacterium Acid fast M. tuberculosis complex
758 views • 31 slides

Bovine tuberculosis. Overview. Organism History Epidemiology Transmission Disease in Humans Disease in Animals Prevention and Control Actions to Take. The Organism. The Organism. Mycobacterium bovis Gram positive bacterium Acid fast M. tuberculosis complex
427 views • 29 slides

Bovine Mastitis. What’s mastitis ?. Inflammation of one or more quarters of the udder. Normal. Inflamed. Mammae = breast -itis = Latin suffix for inflammation. Swelling pain warm redness. What’s the significance of bovine mastitis ?.
3.41k views • 34 slides

Cells that count. The standardizing of diagnostic tests for bovine mastitis Bert Nederbragt Descartes Centre for the History
402 views • 25 slides

Mastitis. Joe Breuner, M.D. Thanks to. Doug Trotter, who gave this talk 18 months ago. Case Presentation. Healthy 25 year-old woman, G2P2, with a 6 week-old infant Infant is fully breast-fed Patient is fatigued due to caring for 2 young children
2.24k views • 35 slides

The antibacterial activity of aqueous and methanol extracts of Punica granaatum L was investigated against bovine mastitis causing bacterial pathogens Streptococcus agalactiae, Staphylococcus aureus, Streptococcus uberis, Escherichia coli, Streoptococcus dysagalactiae and coagulase negative Staphylococcus aureus by agar disc diffusion method isolated locally from clinical cases. The results obtained in the present study scientifically proved and suggest the use of Punica Granatum for treating mastitis causing organism. The phytochemical screening of the plant revealed the presence of alkaloids, tannins, carbohydrates, flavanoids, phytosterols, phenols, sterols, terpenes, and volatile oils. The proximate analysis was carried out.

Bovine Economics. Socialism. You have two cows, and give one to your neighbour. Communism. You have two cows. The State takes both and gives you some milk. Fascism. You have two cows. The State takes both and sells you some milk. Bureaucratism. You have two cows.
247 views • 22 slides

Mastitis. SURENDRA SINGH, 318. Mastitis. An acute inflammation of the interlobular connective tissue within the mammary gland. Mastitis. Normal breast architecture. Outline. Epidemiology Presentation Predisposing factors Microbiology Treatment Complications Effect on breast milk.
520 views • 35 slides